Cancer simply is uncontrolled growth of abnormal cell in the body. Cancer is a large, heterogeneous category of diseases in which a group of cells exhibit excessive and uncoordinated growth, invasion that intrudes upon and destroys adjacent tissues, and often metastasizes, where development of secondary deposit in site distant and discontinuous with primary tumor. Our aim is to make this blog a great source for the people who are interested in cancer.
Significance
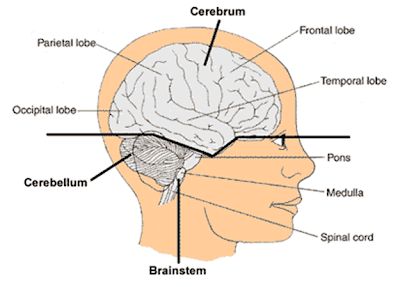
The brain is the center of thoughts, emotions, memory and speech.
Brain also control muscle movements and interpretation of sensory information (sight, sound, touch, taste, pain etc)
Tumors can effect any part of the brain and depending on what part(s) of the brain it affects can have a number of symptoms.
- Seizures
- Difficulty with language
- Mood changes
- Change of personality
- Changes in vision, hearing, and sensation.
- Difficulty with muscle movement
- Difficulty with coordination control
Background
- Estimated 18,400 primary malignant brain tumors will be diagnosed in 2004 —10,540 in men & 7,860 in women.
- Approximately 12,690 people will die from these tumors in 2004.
- Accounts for 1.4% of all cancers
- Accounts for 2.4% of all cancer related deaths
- In adults over 45 years of age 90% of all brain tumors are Gliomas
Gliomas: A general category of cancer that includes astrocytomas, oligodendrogliomas, and ependymomas
Astrocytoma
- Astrocytes brain cells abnormally dividing causing tumors called astrocytomas.
- Astrocytes are glial cells that help nourish neurons– they help repair damage
- How the astroytomas are classified
o How close the cells are together within the tumor
o How abnormal the cells are
o How many of the cells are proliferating
o Whether or not there are blood vessels growing near the tumor
o Whether or not some of the cancer cells have degenerated or not
Astrocytomas--Treatments
- If tumors have not infiltrated normal brain tissue then surgery can be a cure
- Low-grade Astrocytomas are not curable by surgery. However through surgery as much of the tumor as possible is removed and then the patient usually goes through radiation treatment.
- High-grade Astrocytomas are not curable by surgery. After surgery has removed as much of the tumor as possible the patient can go through radiation treatment and chemotherapy.
- Most common drug given to these patients after chemotherapy is BCN
Oligodendrogliomas
- These tumors start in mutated oligodendrocyte brain cells
- Oligodendrocytes make myelin which help neurons transmit signals through the axons
- These tumors may spread through cerebrospinal fluid pathways but typically do not usually spread to locations outside of the brain or spinal cord.
Oligodendrogliomas-Treatments
- Because these tumors infiltrate normal brain tissue these tumors are not cured through surgery. However removal of part of the tumors can relieve some symptoms and prolong life.
- If the tumor is causing disabilities to the patient after surgery the patient may go through chemotherapy, perhaps followed by radiation treatments.
Ependymomas
- Mutated ependymal cells
- Ependymal cells line the ventricles in the central area of the brain and they line part of the pathway through which the cerebrospinal fluid travels
- Theses mutated cells may block the cerebrospinal fluid from exiting the ventricles causing the ventricles to enlarge (hydrocephalus)
Ependymomas-Treatments
- These tumors do not usually infiltrate normal brain tissue and are therefore curable through surgery.
- If surgery is unable to completely remove the tumors the patient may try radiation therapy.
Diagnosis
- These tumors can be detected through a MRI, CT scan or a PET scan.
- Once detected, depending on where the tumor is located, a biopsy officially is used to diagnosis cancer.
Risk Factors
Most brain cancers happen for reasons unknown, however some small risk factors are
- Radiation exposure
- Exposure to vinyl chloride
- Immune system disorders
Prognosis
- For people ages 15-44 five year survival rate is 55%
- For people ages 45-64 five year survival rate is 16%
- For people over 65 five year survival rate is 5%

thnks for your useful information. thats so good.
ReplyDeleteHarga Ganoderma Plus Capsule
Agen Eye Care Softgel Bandung
Manfaat eye Care Softgel Green World
Gastric Health Tablet Green World
thnks for your useful information.and i hope u will update every day. :D
ReplyDeleteManfaat Lecithin Softgel
Gastric Health tablet Green World
Khasiat Cordyceps plus capsule
Harga Ganoderma Plus capsule
Manfaat Ovary Nutrition capsule
Manfaat triflex capsule Green World
Manfaat Eye Care softgel Green world
Cara Pemesanan Ginkgo biloba plus capsule
Agen Eye Care softgel Bandung
Khasiat Braincare capsule